With more and more connections being installed in homes and commercial buildings, Glenn Ward, General Manager of Dunasfern, discusses what is driving our data networking.
We have all seen the wheel of doom circling round and round as we wait endlessly for a connection and demand for data continues to increase year on year, at an alarming rate. We now have more and more streaming devices in our homes, at work and in public spaces. A typical home will have gaming, video, browsers, smart home automation and even doorbells requiring and sending data and home automation is forecasted to grow at 10% per year.
Not only is demand increasing at a rapid rate, our demand for faster connection and greater capacity is also growing fast and acceptance of smart home automation is fuelling this growth.
Just as we have become accustomed to new ways of transacting and connecting since the start of the pandemic, so too have we accepted online collaboration and remote working as the norm. The workforce will continue to be hybrid, with employees working fully from home or in the office or dividing their time between these locations.
For network teams, this means having to support thousands of “unique” network locations and connections in this hybrid work environment. In addition, they need to ensure that the network can manage a significant increase in voice and video traffic, enable a more seamless and personalised user experience (UX), no matter where users are, and support the performance of business applications.
We have come a long way since the invention of Morse code over the telegraph. So, in today’s digital world, where staying connected is super important for households and businesses alike, how data networks are changing is important and in today’s fast-changing digital world, we need to expand data capacity and a big part of this is data networking.
Definition of data networking
Data networking is all about creating, setting up, and looking after networks that help share information. It involves using different technologies like Ethernet, TCP/IP, and Wi-Fi, which are like building blocks for today’s networks. These networks can be small, like in one place (called LANs), or big, stretching across many places (known as WANs). With more businesses using cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), good data networking is critical.
Data networking supports a wide range of functions, including remote work arrangements, real-time collaboration, e-commerce transactions and smart home automation. Businesses continue to digitise their processes and embrace emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
The future of data networks will be defined by the key trends and technologies. Software-Defined Networking (SDN) offers more flexibility and agility in network management by separating control from data and SDN lets organisations change network settings and allocate resources quickly as needs change. Edge computing and 5G technology will also transform data networking. Edge computing moves computing closer to users, while 5G offers super-fast speed and bandwidth.

The Evolution from 4G to 5G
5G technology represents a significant advancement over 4G networks in terms of speed, latency, and capacity. Unlike 4G, which primarily relies on traditional cellular towers, 5G utilises a combination of frequency bands, including millimetre-wave frequencies, for more efficient data transmission. This transition allows for faster data transfer rates and improved performance, making it suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications like virtual reality and augmented reality.
5G technology is super-fast and has very little delay, with download speeds up to 20 gigabits per second (Gbps) and only 1 millisecond (ms) of delay. It lets you do things in real-time, like watching videos, playing games online, doing surgery remotely, and even driving self-driving cars. 5G can also manage lots of things connecting at the same time without slowing down, which means more gadgets like smart devices and IoT that can work together smoothly.
In healthcare, 5G helps monitor patients from afar, offers doctor appointments online, and enhances medical scans, making healthcare easier to access and improving patient health.
The transportation sector benefits from 5G by making self-driving cars, smart traffic systems, and vehicle-to-everything communication possible, which boosts safety and makes travel more efficient.
5G also transforms manufacturing by creating smart factories. Here, devices connected to the internet and powered by artificial intelligence improve production and make it more efficient.
The exponential growth of IoT devices across various sectors is driving the need for robust networking solutions. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT devices are becoming the norm and contributing to the data explosion and this proliferation presents challenges in scalability, security, and data management for traditional networking architectures.
The smart home revolution
The explosion of smart home technologies is where innovation meets convenience and transforms the way we live. From lights that respond to your voice commands to security systems that ensure peace of mind, smart homes are redefining our relationship with technology and growing the need for greater speed and capacity in our data networks and companies worldwide continue to create new and exciting ways to make our homes safer and more efficient.
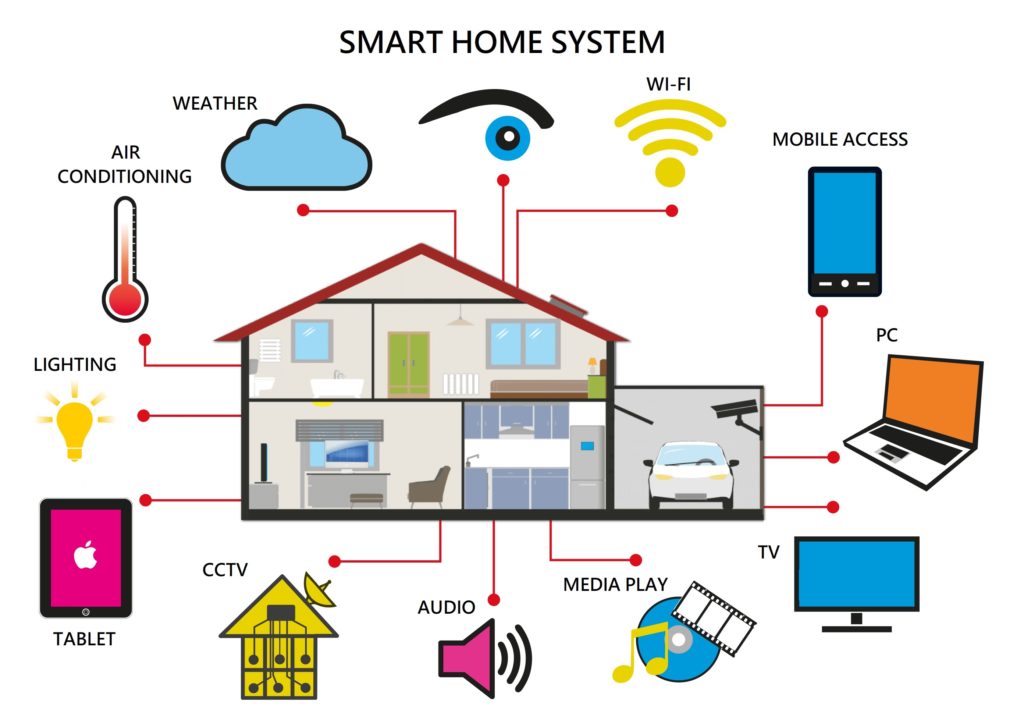
Voice-controlled smart home devices like Amazon’s Alexa and Google Assistant are gaining popularity, simplifying tasks for millions of households. This surge highlights the increasing reliance on voice as a primary means of interacting with technology at home. Meanwhile, the advent of smart home security systems equipped with advanced computer vision and facial recognition is revolutionising home security. These systems can distinguish between family members and intruders, offering customised alerts and bolstering security and convenience. Notably, software incorporating these technologies is expected to see rapid growth, at 11.5% per year. Additionally, the emphasis on interoperability and open standards in the smart home sector is fostering compatibility between devices from different brands, empowering consumers to create comprehensive smart home setups tailored to their preferences.
As technology improves and becomes more affordable, more and more people are finding smart home gadgets helpful and convenient for everyday life. Whether it’s for saving energy, increasing security, or just making life easier, the growing acceptance of smart home technology shows that it’s becoming a normal part of modern living.
The future of data networking is continuing to evolve because of new trends and technologies like Software-Defined Networking, the Internet of Things, SMART home automation and 5G. It’s crucial for consumers and businesses to embrace these changes to succeed in the digital age and by keeping up with these advancements and using them well, we can all improve our work, home environments, and find new chances to grow in a more connected world.
Find out more here
Find more feature articles here

